Historical Cost Principle Historical vs Fair Value
Content

When you buy assets for your small business, you need to account for them in your books. The cost principle is a simple method for managing the value of your long-term assets. Contrary to that statement, if financials were reported on the basis of market values, the constant adjustments on the financial statements would cause increased market volatility as investors digest any newly reported information. Under the Historical Cost Convention, assets and liabilities are initially recorded in the accounting system at their original or historical cost and are not adjusted for the subsequent increase in value. Historical cost is a term used in accounting that represents the original cost of an asset you’ve acquired or purchased at the time of transfer or sale. In cost accounting, the term refers to an amount of money used to buy or run a business.
- For example, costs expended to place the company logo on a delivery truck or to expand the space on a warehouse would be capitalized because the value they provide will extend into future accounting periods.
- Under the historical cost concept, business transactions are recorded at the original cost at the time of the transaction.
- Both of these terms are used to describe the costs of an asset at the time the asset is purchased or acquired.
- However, historical cost has the disadvantage of not necessarily representing the actual fair value of an asset, which is likely to diverge from its purchase cost over time.
It is a key feature of accounting and bookkeeping, as outlined by the cost principle. The primary advantage of historical cost is that it curbs any tendency for the business to overvalue an asset. As an added reality check, while appreciation is ignored in historical cost, amortization and depreciation of an asset is not.
Book Value of an Asset and Historical Cost
If one purchased a building in 1955 for $20,000 and market prices have brought the value of that building to a solid $875,000, stating that its value is $20,000 is unnecessarily conservative and misleading. For certain classes of financial instruments, where there are markets that can provide real-time quotations of assets exactly like the ones held in a financial services firm’s books, using historical cost borders on the absurd. Historical cost is the original cost of an asset, as recorded in an entity’s accounting records. Many of the transactions recorded in an organization’s accounting records are stated at their historical cost.
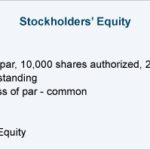
If the sale results in a gain, the excess received over the building’s net book value is disclosed on the income statement as an increase to the accounting period’s income. If the sale results in a loss and the business receives less than book value, the loss is also disclosed on the income statement as a decrease https://kelleysbookkeeping.com/ to income. Any valuation basis other than historical cost may create serious issues for companies. For example, if a company uses current market value or sales value rather than historical cost, each member of accounting department is likely to suggest a different value for each asset of the company.
What assets are excepted from historical cost?
However, the company books show the current value of the machine as $50,000 ($60,000 cost of the machine minus the accumulated depreciation over 2 years of $10,000). The fair market value of that property is easily above $300 million in 2020. According Historical Cost Definition to the cost principle, the purchase must be recorded on the date of its occurrence at the cash amount paid. In this case, even though the invoice was received on a different date, the record date must be the one at which the purchase occurred.
What is standard cost vs historical cost?
Costs used: Standard costing includes cost figures that are predetermined based on past experience and expert advice. In historical costing, data are included from costs that have actually been incurred.
Historical cost is the purchase price of an asset, whereas fair value is the estimated market price of an asset. Use of historical cost prevents the over-valuation of an asset; this can be particularly useful when asset appreciation is due to volatile market conditions. However, many financial experts argue that historical cost may be too conservative a value for assets because the sum is not adjusted even in stable market conditions.

